The Current State Of US Fusion
Introduction:
In November, I got a call from a podcaster. His name was Gabe. He was curious about fusion. Gabe “…want to do an energy show and contrast
fusion with new fission. I honestly know
very little about it…” Questions were
sent along and I spent a weekend researching a reply.
Fusion is heating up. Activity and interest has been steadily
rising over the past fall. Yes, ITER
keeps on rolling - but a lot of people are looking elsewhere. Since September, I have personally heard of
several new small efforts, a new lobbying group and two new investor forums [49
- 52, 34, 35].
But, where is all of this heading? Will these folks still be here in 5 years? Have we seen the winning technology already? The answers to these questions are still
unclear. What is clear is the need to remain
scientifically accurate. If you see a technical
error, please reach out. As Warren
Buffet famously says: “be fearful when others are greedy”. When others get enthusiastic, technical
people should stay conservative.
I cannot say when fusion power will
come. I can say that there are a lot of ambitious,
intelligent people aiming to try.
Moreover, there are lots of ideas that have not yet been tested. And, there are investors looking to make big waves. Exciting.
These next few years should be damn exciting. Hope you stick around.
Could you give us a synopsis of where fusion power research is at and
where it is going?
US Fusion Budget:
The US
fusion budget last year was 951 million dollars [1]. For comparison NASAs’ budget was eight
billion [2]. I argue that the current
fusion budget is very low and lopsided.
It is lopsided because it focuses only on two approaches - which we know
will not become commercial. It is low,
because this budget gives us no space for anything new. Sadly, this has been the state of things for
about the last 20 years or so. Below is
a plot of the US fusion budget.
Laser fusion (ICF):
The
US fusion budget gets split in half. Half of the money is sent out to support laser
fusion and related technologies. The
main goal of that money is to maintain the status quo. It holds up activity at the national labs, a
few companies and a few universities. Laser
fusion is where you take a small ball of ice and you blast it. The ball of ice is frozen radioactive
hydrogen. The beams attack from multiple
(60 or 192) directions and squash the fuel [3, 4]. When the beams hit the ice surface, there is
an explosion of energy outwards and an equal and opposite compression wave
inwards. This compresses the fuel to a
temperature and pressure where fusion can occur. For example, a typical temperature could be between
10 and 15 million degrees kelvin and the pressure is 1000x the density of water
[3, 4]. A typical implosion would last
about 20 nanoseconds.
This
laser approach to fusion is over sixty years old [5]. For the first ten years it was classified by
the US government. The effort became
public in 1972 [6]. Since then we have built
a couple dozens of these kinds of machines.
The government likes this approach because aside from doing fusion you
can replicate the environment inside a nuclear bomb. I spent six years working on this fusion
approach. My doctorate was on developing
these ice balls – known as targets - trying to find ways to create them in a
cheaper way.
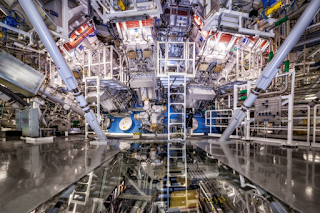
A picture of the National Ignition
Facility – a very expensive ICF system.
The biggest laser facility in the world is the National Ignition Facility. This machine was built at Livermore National Labs. Construction started in 1997 and it took them 12 years to build. The thing cost 3.8 billion dollars and was first turned on in 2009 [3]. The key idea behind NIF was getting something called ignition. Ignition is a fusion chain reaction. You get 1 fusion event, and that creates another, and another, and another. That is a big deal - if you can make it to work.
Well, in 2016, the Department Of Energy admitted that NIF will never ignite [7]. That was a big deal. What it means is that laser fusion is probably not going to work as a power plant approach. You cannot get enough energy out of the machine to overcome the huge energy you put in. NIF is probably somewhere between 3 and 0.5% efficient [8]. Moreover, this is a major defeat more than just one approach. There is a whole family of laser fusion-like approaches that are very closely related. Some concepts include: direct drive, indirect drive, ion drive fusion and fast ignition [9, 3, 4, 10]. All of these ideas suffered with NIFs’ failure to get ignition.
So bottom line: we are spending 440 million on a spectrum of groups, companies and universities following an approach that we know will never work. It will not work energy-wise nor will it work commercially. That may have been fine when there were no other fusion approaches available to us – but that is no longer true.
Tokamaks:
The
rest of the US fusion budget goes to a family of magnetic schemes surrounding
the tokamak. A tokamak is basically a
racetrack. If the ions are the cars,
then the course is set by the magnetic fields.
The ions race around, and around, the ring. Hopefully they bump into one another at high
speeds. When they do this, they can
fuse.
The
tokamak is the world-wide fusion research heavyweight. Over 220 tokamaks have been built, planned or
decommissioned since this field got started [11]. Today, we are reaching a point where 80% of
all the fusion researchers in the world - are all tokamak people. That is a problem. The program directors, the reviewers and the
university professors are mainly looking at fusion through the lens of a
tokamak; through the physics of a tokamak.
This means they have a mostly hazy understanding of other approaches.
Not to say that
tokamaks have not worked well. For
example, the world record for the longest running tokamak is 26 hours. That was set by a startup in England [12].
Technically, the world record for energy extraction,
in fusion, is held by a tokamak. The
record was set by a machine called JET, in England in the late nineties. That record?
23 percent. That machine took 100
megawatts to run [48] and it pulled 23 megawatts out of the plasma. It is worth pointing out that the JET team
claimed a much higher efficiency. But,
they were playing math games (NIF did the same thing in 2014). They used the energy on plasma as their
starting point – not the real input numbers.
Finally, a good example of a typical tokamak performance was set by
China. They ran their machine for 102
seconds at 50 million degrees [13]. That
is considered very strong showing in the tokamak world.
A picture of the ITER site.
Right now, the world is building a huge tokamak in France, called ITER. This project is the focus of most of the US fusion effort. ITER work is being done in many states across the US. Multiple companies, organizations and universities are involved. Ultimately, we don’t know how much this is going to cost, but estimates range from 16, 21 and even 50 billion dollars [14 - 17]. Currently ITER is 7 years delayed [18]. I suspect that it will be NIF all over again. They will finish it. It may work - or it may fail physically - but it will never work commercially. I doubt it will produce more energy than we put in it. We heard this same story for 12 years with NIF – and that machine failed. There are basic flaws with these huge machines. It takes so long to build them - that innovations cannot be added as construction occurs. They are also very complex – hiding problems within the technical details. They also rely on models that can make assumptions that turn out to fail. That said ITER will drive technology into the greater economy – even if it fails.
US Fusion Funding Problems:
1. A professor or a team comes up with a good idea.
2. They publish. They get a small (100K to 500K) grant.
3. They run a lab for 5 to 10 years. They makes huge strides.
4. They get to a point where they need 1 to 5 million in funding.
5. Their funding gets killed support existing approach (NIF or ITER). Idea dies.
This has happened time and time again. It is still happening now. Here are some (rough) examples from the past 20 years. Note there are examples for concepts further back.
- The Levitating Dipole Experiment at MIT from 1998 – 2011. This was run by Dr. Jay Kesner and Dr. Micheal Manual [19]. The team was gearing up for ignition experiments when funding was cut - for ITER - in 2011.
- The Dynomak at the University Of Washington, run by Dr. Tom Jarboe. In 2011, the group found a great way to heat plasma. This opened up a whole new approach to spheromaks [20]. They could not get the funding and so went private.
- The POPS machine proposed by Dr. Park and a team at Los Alamos in 1998 [21]. This concept played games with ion oscillations to avoid the fusor grid.
- The penning trap concept pushed by Dr. Dan Barnes (LANL) late nineties. Dr. Barnes wanted to trap a mostly negative plasma inside a penning trap and get the ions to accelerate using the created voltage drop [23].
- A multiple ion beam approach pushed by Dr. Ray Sedwick at the University of Maryland in 2011. This approach has some fundamental charge limitations and instabilities – but Ray was able to get pretty far with it [22].
- The Plasma Liner Experiment pushed by Dr. Hsu at Los Alamos and by Dr. Doug Witherspoon at HyperV Inc. This concept used converging plasma beams to squash plasma together. This has been around since the early 2000’s.
- The Field Reversed Configuration work done at the Redmond Plasma Physics Lab in Seattle. This group existed through the nineties and was run by Dr. Alan Hoffman & Dr. John Slough [25]. When they could not get any more DOE funding, they formed two private companies.
- The Princeton Field Reversed Configuration. Dr. Sam Cohen at PPPL set a world record for the longest stable FRC ever created by mankind [26] but he runs his lab on less than 200k a year. This year, the DOE ended their funding (to support ITER) and they had to go through NASA and the Army.
One example of a new fusion concept. The University of Maryland modeled this approach, but this failed because of space charge limitations, problems with ions flying apart (beam-beam instabilities) and problems at the turning radius [26, 27]. This approach attempted to amplify a natural ion-ion beam bunching effect. It borrowed innovations from the field of mass spectroscopy.
In fact, in the
60 years since we first demonstrated controlled fusion, there have been many
ideas put forward to turn it into a power plant. In the chart below, I lay out these ideas. I have grouped them together by approach. Even this list is probably incomplete. Recently Dr. Ralph Moir has suggested several improvements
to this chart [A-FF]. Bottom line: our current US funding system is great at
maintaining the “fusion status quo” but sucks at adding anything new.
A New System:
If we ever want to get to a commercial plant - we need a new funding system. The US should adopt a system similar to the one used in pharmaceutical companies. Drug companies have a pipeline. They give a bunch of high risk drugs a very small amount of money. These could fail. So they support many concepts – but keep things cheap. A good amount might be a million a concept. That is typically more than most teams survive on. A second tier should be supported at the 10 to 30 million dollar range. You could support maybe ten concepts there. These are more mature designs. Finally, there should be three big efforts that should be funded at the 100 to 150 million range. This way you could incorporate your existing efforts, while adding in new ideas. For example, ITER and NIF could get 100 to 150 million per year in this system. But you could add a new big machine, like a national FRC.
Critically, you must build this system around going commercial. The money must be tied to this. Right now, all we care about in fusion is something called a triple product. That is the density x temperature x trapping time of a machine. This is a terrible meter stick. By that definition NIF is a great machine – even though it costs 3.8 billion and failed to get ignition.
We should care about a machines: run time, cost, efficiency, energy in/energy out and size. Groups must to prove they are making progress along these lines - to move up or down in funding. Below is a quick graphic I threw together on this. Finally, it would be nice to try to fund with public-private partnerships. Use public money to try to lure private investors. There are some interesting co-ownership models you could pursue. For example you could have a privately run group applying for public funds through block grants.
Amateur Fusion:
Since
2000, fusion has been moving in new directions, which I think are worth
watching. These are outside of the
federal system. New innovations have
come from two groups: amateurs and venture capitalists. I will start with the amateurs. The first private citizen to build a fusion
machine was a guy named Richard Hull.
He was living in Richmond Virginia and in 1999, Richard built a small
fusor in a shed behind his house. He got
fusion. This was a pivotal moment in the
history of fusion – and almost no one noticed.
It paved the way for people to start doing fusion in their homes. A
fusor uses an electric field to heat ions to fusion conditions. Typically you need between 10 and 110
thousand volts to make them work. They
have a big metal cage in the center.
This sucks away mass and energy from the device. Typically the losses are 10,000 to 1. Meaning, for every unit of energy of fusion
we make we are losing about 10,000 to that wire cage [38].
We have now seen amateurs build other devices, other than fusors. To be clear: none of these machines have
gotten any fusion yet. But, we have seen
an amateur field reversed configurations [36], amateur spindle cusps [34] and I
know of one group trying to build an amateur compact stellorator [35]. These are all unique fusion machines –
devices we’ve never seen outside of university labs – being built by
hobbyists. The reason for all of this is pretty
simple. Amateurs can do this now
because of superconductors. That
technology has now reached a point where you can get a strong field, for a
reasonable price and a small electrical energy.
In the case of high temperature magnets, you can run them at reasonably
cold temperature using liquid nitrogen.
Often times, these kids can get the stuff they need for free. The companies are willing to hand over the
magnets for free.
Venture Capital:
The
other big company is Tri Alpha Energy, which has a partnership with Google [42]. The company has gotten funding from Peter
Theil and Steve Balmer from Microsoft.
This company dates back to 1998 and it has an approach based on the
field reversed configuration [41]. The
FRC is a self-sustaining plasma donut.
The plasma moves in a loop. That
movement makes a magnetic field. That
field self-sustains the donut. The FRC
is an example of a self-organized plasma.
I think self-organized plasmas are the direction this whole field needs
to move in. The FRC is great. The problem with it is stability. The loop slows, and flies apart. Tri Alpha has to keep its’ plasma spinning by
hitting it with particle beams along its’ surface. Like the old game of the hoop and the
stick. Last I heard, they were able to
keep the donut spinning for 11 milliseconds [43]. That might not sound like a long time, but
this was kept moving for the lifetime
of the machine. Meaning if they build a machine that can run for 2 hours, they
may get 2 hours of fusion.
Behind
these two big companies, there are about a dozen smaller groups. I like CT fusion from the University of
Washington. I like EMC2 which just did
some groundbreaking simulations on the polywell. I also like Lockheed Martin’s CFR machine,
but I urge them to publish. I also think
Tokamak Energy is doing very well. There
are more groups that need to be watched.
Fusion, On The Market
Finally,
I want to mention that there is now a commercial product on the market that
uses fusion. For a bit over a million
dollars, you can buy a neutron generator from a company called Phoenix Nuclear
Labs [45]. Neutron generators based on
fusion are not new. We first saw them on
the market back in 2000, from a company called NSD-Gradel. But
this PNL machine is light years ahead of where they were. The device can produce 1E+11 neutrons per
second, for over 130 hours continuously [44].
Along with another company, PNL is gearing up to use these devices to
mass manufacture medical isotopes. That
market is about 1 billion dollars a year worldwide, and these companies are
going to crush it. They signed a 110
million dollar deal with GE Health care and a distribution deal with Chinas’
largest pharmaceutical company [45]. In
August, Shine broke ground on a new facility to manufacture these isotopes
[45].
I’ve heard it said that
fusion power has the potential to give us limitless free energy one day. In your opinion, how likely is that to happen
and how far off might that be?
The
milestone in front of everyone is net power.
That is like that first lift off at Kitty Hawk. No one has done it yet. Not in sixty years. Not anywhere in the world. We have known since 1956 what it will take to
get there. A British man named John
Lawson is too thank for that. In 1956,
John worked out the energy balance for any plasma-based fusion device [28]. Here it is below.
All you got to
do is build a machine to beat this equation and you’ve made history. Net could mean 101 watts out of a 100 watt
input. All it means is more energy out
than you put in. I have written
extensively about each term in this equation, and what kind of design
principals it means for a fusion device.
- Fusion rate is self-explanatory. So far, much of the world has focused solely on this, by driving at triple product.
- Conduction. This is all the energy that leaves with the mass. Metal is the enemy here. When plasma touches metal - it leaks out. This robs energy from the machine, killing it’s’ efficiency. Hence you need space around your plasma. You also want a strong trap to keep the plasma away from the walls. Lockheed Martin is following a long shot approach to make a near perfect magnetic trap – which if it works – would be a big break through [29 -33]. Foolishly, Lockheed has not published so we do not know where they stand. I have even seen people build their chamber out of insulators like glass to stop conduction losses [25].
- Radiation. This is all the energy leaving the plasma as light. Plasma bleeds energy away, as light. People have talked about reflecting that light back into the plasma – but that idea is very, very limited. For example is almost impossible to reflect an X-ray. Another option is to drive up your density. That could slow light loss. Personally, I think your best bet here is trying for a tuned plasma. In a perfect world you would want a plasma with lots of really cold electrons and a few hot ions. That would be best. This kind of distribution may not be possible [29]. It is not clear at this point. Energy distributions in plasma are a function of many other things: shape, structure, magnetic and electric fields, injection, runtime, ect…. Could you tune your plasma? IDK. We need to get hard data proving this one way or the other.
- Efficiency. This is how well your device spends or collects energy. There has been some exciting work done here. In 1982, a team a Livermore was able to capture 48% of the energy coming off a fusion reactor using something called direct conversion. Basically direct conversion works by putting the charge particles coming off the reactor directly into a wire.
When will
fusion happen? I cannot say for
sure. But I can say that impossible
problems have been solved in the past.
150 years ago, human powered flight was considered impossible. Every expert said it could never be
done. The general public saw it as
impossible. Meanwhile - in the
background - a small group of innovators were trying everything they
could. All kinds of wild ideas were
tried. Lots of failures happened. No one was paying attention. And then, suddenly, two guys who did not have
a formal education and whom no one had ever heard of, created flight. So impossible problems? Sometimes they can be solved.
From what I understand the
only waste product of nuclear fusion is helium. Given our critical shortage of
helium is a worthwhile goal to create a fusion reactor for the purpose of
creating helium economically?
Here
are a few issues with that idea. If you
run the deuterium through a fusor, you will lose a lot of mass in the
process. If you fuse the gas slowly, you
could probably drive up the efficiency of that process. You could steal some other ideas from the
fusor world – POPS or magnetically insulated fusors – to help out. Instead of a fusor, you could consider moving
to a beam on target, or even beam on beam process. Making a deuterium target is costly because
you would need to cool and compress the gas into either a liquid or solid
target – that is not cheap. The
beam-beam approach has instabilities to deal with.
If
you got the fuel to fuse, your biggest issue then becomes dealing with the
tritium, a byproduct of this process. One
option would be to sell the tritium to someone who would buy it (say a
government lab like Savannah River). You
would make far more money on selling the tritium than the helium – tritium is far
more lucrative. Dealing with the tritium
in the US is a huge pain. Where I got my
PhD, it took a team of 20 engineers, 4 years and 12 million do deal with our
tritium handling system. There was EPA
and NRC permits, air monitoring and recovery.
That is a regulatory/cost nightmare.
On top of the fusion issues, you will have gas compression to deal
with. Either cleaning up the feed or the
results of the fusion. I think you should ask a compressed gas expert about
this. I do not know if anyone has done a
cost analysis on this business model. It
would all hinge on the differences between the gas prices.
How is it possible for a
fusion reactor to control the heat of a fusion reactor without wearing out from
the stress? What accidents are possible?
That depends on which
fusion approach wins. Right now I cannot
say what a fusion power plant will ultimately look like. Most systems keep their plasma spaced out –
away from the walls – so if the energy leaks out, it will dissipate in power. That precaution keeps many machines away from
any big meltdowns. The likely accident
would depend on which approach wins.
· Tokamak:
If a fusion plant looks like a tokamak with superconducting magnets - then
there are known problems. A
superconductor can “become normal”. This
breaks the magnetics and lets the hot plasma lose. It has happened 17 times in tokamaks [46]. It also happened at CERN and cost them like a year
in work.
· Laser: If a laser system
wins - there would be little chance of a meltdown. There is barely any plasma in the laser
machine. An accident there would like be
a laser beam firing off and hitting something.
Another accident in the laser system could be a tritium leak.
· Beams: If a beam system
ends up winning, a plasma leak is also unlikely. The reason is that beams have almost no
plasma in them.
· Cusp: If the plant ends up looking similar to Lockheed Martin’s approach,
then plasma leaking is worth thinking about.
Lockheeds’ approach also has superconductors just like the tokamaks –
they could also suddenly lose their super conductivity, “go normal” and break. That would release hot plasma.
Could fusion power be a workhorse
for moving man into space both cleanly and cheaply?
Yes, I think fusion could have a major impact on spaceflight. There are two basic plans for a fusion driven rocket. In plan one, you put a fusing plasma at the apex of a parabola, at the back end of a ship. This material escapes the fusing core at high speeds, bumps against the ship wall and shoots off in one direction. This pushes the ship forward. In the second plan, you have a cavity at the back of the ship. Plasma get sped way up as it passes by a fusing core. The plasma has to shoot through a tiny hole in the back. As it does it flies out very quickly.
There are
currently a few NASA funded efforts to look into this:
· The
University of Maryland got some money to look at using a fusor as a space
engine.
· A
company called MSNW has raised about a million dollars to try to do this with a
field reversed configuration.
· A
company called Princeton Satellite Systems has a 500K grant with Sam Cohen a
Princeton professor who has built a rotamak.
Sam has the world record for the longest stable FRC ever created (300
milliseconds). They predict 100
kilometers per second of thrust. This
could get you to Mars in a matter of weeks.
References:
1. “The US
Fusion Budget.” Fusion Power Associates, 12 Dec. 2016, aries.pppl.gov/FPA/OFESbudget.html.
2. Dunbar,
Brian. “Budget Documents, Strategic Plans and Performance Reports.” NASA, NASA,
27 Jan. 2015, www.nasa.gov/news/budget/index.html.
3. “National
Ignition Facility.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 9 Nov. 2017,
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Ignition_Facility.
4. University
of Rochester - Laboratory for Laser Energetics. “About OMEGA.” OMEGA Laser -
Laboratory for Laser Energetics, www.lle.rochester.edu/omega_facility/omega/.
5. Kidder, Ray
E. “Laser fusion: the first ten years 1962-1972” High-Power Laser Ablation,
1998, doi:10.1117/12.321569.
6. Nuckolls,
John, et al. “Laser Compression of Matter to Super-High Densities:
Thermonuclear (CTR) Applications.” Nature, vol. 239, no. 5368, 1972, pp.
139–142., doi:10.1038/239139a0.
7. Clery,
Daniel. “NIF May Never Ignite, DOE Admits.” NIF May Never Ignite, DOE Admits,
16 June 2016, physicstoday.scitation.org/do/10.1063/PT.5.1076/full/.
8. Moses,
Edward I. "The National Ignition Facility: Exploring ICF Burning Plasmas
In the Laboratory." Presentation to the American Association for the
Advancement of Science. Washington DC. 18 Feb. 2005. Slide 29. Lecture.
9. “Fast Ignition.”
Fast Ignition,
lasers.llnl.gov/science/ignition/fast-ignition.
10. Hershely,
Charles. “Ion Beam ICF.” Fusion Power Corporation, www.fusionpowercorporation.com/.
11. Nick.
“All-the-Worlds-Tokamaks.” All-the-Worlds-Tokamaks, July 2006, www.tokamak.info/.
12. Energy,
Tokamak. “We Now Hold the World Record for Running Our Tokamak with Magnets of
High Temperature Superconductors for 29 Hours!” Tokamak Energy, 6 July 2015, www.tokamakenergy.co.uk/we-now-hold-the-world-record-for-running-our-tokamak-with-magnets-of-high-temperature-superconductors-for-29-hours/.
13. “China's
'Artificial Sun' Sets World Record with 100 Second Steady-State High
Performance Plasma.” Phys.org - News and Articles on Science and Technology, 6
July 2017, phys.org/news/2017-07-china-artificial-sun-world-steady-state.html.
14. "ITER - the Way to New Energy."
ITER Project Milestones. ITER, 2013. Web. 06 Oct. 2015.
15. Cho, Adrian. "Cost Skyrockets for
United States' Share of ITER Fusion Project." Science Insider.
Science/AAAS, 10 Apr. 2014. Web. 27 Oct. 2014.
16. "Currency Calculator Converter Euro to
US Dollar." Currency Calculator (Euro, US Dollar). X-Rates, 27 Oct. 2014.
Web. 27 Oct. 2014.http://www.x-rates.com/calculator/
17. "Fusion Furor." Nature.com.
Nature Publishing Group, 23 July 2014. Web. 27 Oct. 2014. http://www.nature.com/news/fusion-furore-1.15596
18. Gibne, Elizabeth. "Five-year Delay
Would Spell End of ITER." Nature.com. Nature Publishing Group, 31 July
2014. Web. 06 Oct. 2015.
19. Kesner,
Jay. “A Phone Call with Dr. Jay Kesner.” 15 Dec. 2013.
20. Jarboe,
Thomas. “Steady Inductive Helicity Injected Torus (HIT-SI).” Aeronautics and
Astronautics, December 2016, www.aa.washington.edu/research/HITsi.
21. Park, J.;
et al. (2005). "Experimental Observation of a Periodically Oscillating
Plasma Sphere in a Gridded Inertial Electrostatic Confinement Device".
Phys. Rev. Lett. 95: 015003. Bibcode:2005PhRvL..95a5003P.
doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.95.015003. PMID 16090625.
22. Chap,
Andrew M., et al. “A Particle-in-Cell Simulation for the Traveling Wave Direct
Energy Converter (TWDEC) for Fusion Propulsion.” 49th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint
Propulsion Conference, Dec. 2013, doi:10.2514/6.2013-3912.
23. Chacaon,
L., and D. C. Barnes. “Stability of Thermal Ions Confined by Rigid-Rotor
Electron Clouds in Penning Fusion Systems.” Physics of Plasmas, vol. 7, no. 11,
2000, pp. 4774–4777., doi:10.1063/1.1312822.
24. Hoffman,
Alan L. "The TCS program - Translation, Confinement, and Sustainment of
FRCs - Final Report." The Redmond Plasma Physics Laboratory Web. 27 Apr.
2017.
.
25. Cohen, Sam,
and B. Berlinger. "Long-pulse Operation of the PFRC-2 Device." The
Joint US-Japan Compact Torus. Wisconsin, Madison. 22 Aug. 2016. Lecture.
26. “Private
email” Dr. Andrew Chap, Dr. Robert Terry and Dr. Matt Moynihan, November 7th
2017.
27. “An Interview with Dr. Alex Klein” A Klein, www.thefusionpodcast.com May 2016.
28. "Some
Criteria for a Power producing thermonuclear reactor" John Lawson, Atomic
Energy Research Establishment, Hanvell, Berks, 2nd November 1956.
29. Rider, Todd
Harrison (June 1995). Fundamental limitations on fusion systems not in
equilibrium (PDF) (Thesis). Massachusetts Institute of Technology. OCLC
37885069.
30. McGuire,
Thomas. Magnetic Field Plasma Confinement for Compact Fusion Power. US Patent
Application, assignee. Patent 14/242,999. 2 Apr. 2014. Print.
31. McGuire,
Thomas. Magnetic Field Plasma Confinement for Compact Fusion Power. World
Intellectual Property Organization, assignee. Patent WO 2014/165641 A1. 9 Oct.
2014. Print.
32. S, Eric.
“Compact Fusion Research & Development.” YouTube. Lockheed Martin, 15 Oct.
2014. Web. 01 Nov. 2014.
33. McGuire,
Thomas. Heating Plasma for Fusion Power Using Magnetic Field Oscillations.
Baker Botts LLP, assignee. Issued: 4/2/14, Patent 14/243,447. N.D. Print.
34. “Private
conversation with Tanner Horne on Spindle Cusps” October 5th 2017.
Tanner Horne and Dr. Matt Moynihan.
35. Thomas,
Scott. “Stuyvesant High Schools’ Compact Stellarator.” Indiegogo, Aug. 2017, www.indiegogo.com/project/preview/f9e0cd7c#/.
36. “Stuyvesant
High Schools' Field Reversed Configuration” YouTube, YouTube, 22 June 2015, www.youtube.com/watch?v=sA70ewxSv28&feature=youtu.be.
37. Schatzkin,
Paul. “Doug Coulter’s Solar Powered Star In A Jar.” Fusornet, 15 Oct. 2015, www.fusor.net/doug-coulters-solar-power-star-in-a-jar/.
38. Miley,
George H., and S. Krupakar Murali.” Inertial Electrostatic Confinement (IEC)
Fusion”, Dec. 2013, doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-9338-9_12.
39. Moynihan,
Matthew. “The Polywell Blog.” An Industry Emerges, 15 Jan. 2015, www.thepolywellblog.com/2015/01/an-industry-emerges.html.
40. Lebarge,
Michele. “General Fusion Updates.” ARPA-E Updates, Aug. 2017,
doi:https://arpa-e.energy.gov/sites/default/files/ARPA-E%202017_ML_web.pdf.
41. “Tri Alpha
Energy.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 12 Nov. 2017,
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tri_Alpha_Energy.
42. Baltz, E.
A., et al. “Achievement of Sustained Net Plasma Heating in a Fusion Experiment
with the Optometrist Algorithm.” Scientific Reports, vol. 7, no. 1, 2017,
doi:10.1038/s41598-017-06645-7.
43. Jaspers,
Roger. “Introducing Alternative Fusion Concepts: Tri Alpha Energy.” EUROfusion,
27 June 2016, www.euro-fusion.org/newsletter/tri-alpha-energy/.
44. Pfeiffer,
Greg. “The world’s most compact neutron generator” Phoenix Nuclear Labs, Sept.
2014. Web. 27 Oct. 2014.
45. “Phoenix
Nuclear Labs Blog.” Phoenix Nuclear Labs, July 2017, www.phoenixwi.com/.
46. Hirsch,
Robert L. “Fusion Research: Time to Set a New Path.” Issues in Science and
Technology, 4 Sept. 2015,
issues.org/31-4/fusion-research-time-to-set-a-new-path/.17
47. “Private Conversation with Carl Genenger and
Matt Moynihan” September 2015, Federal
Way Washington.
48. "JET
Question" Private Email with Dr. Mark Henderson, Electron Cyclotron
Section leader, ITERganization, June 23 2017.
49. Holland, Andrew. “The American Fusion Project.” American
Fusion Project, American Securities Project, 1 Nov. 2017,
americanfusionproject.org/.
50.
Hadley, Malcomb. “Strong Atomics, A Fusion VC Fund.” About Us,
strong-atomics.com/.
51.
“Fusion Is the Future.” 2017 Fusion
Forum. The Alberta Fusion Technology Alliance, The University of Alberta, 4
Nov. 2017, www.acfta.ca/fusion-forum/.
52.
Panel. “Nuclear Fusion: Reacting To
Commercialization.” Stanford University, Stanford. https://www.vlab.org/Events/Nuclear-Fusion/,
Venture Labs, 14 Nov. 2017.
Chart Citations:
A. "The
dynomak: An advanced spheromak reactor concept with imposed-dynamo current
drive and next-generation nuclear power technologies" Fusion Engineering
and Design,Sutherland, Jarboe, Morgan, Pfaff, Lavine, Kamikawa, Hughes,
Andrist, Marklin
B. Jarboe,
T.r., B.s. Victor,B.a. Nelson, C.j. Hansen, C. Akcay, D.a. Ennis, N.k. Hicks,
A.c. Hossack, G.j.Marklin, and R.j. Smith. "Imposed-dynamo Current
Drive." Nucl. Fusion Nuclear Fusion 52.8 (2012): 083017.
C. McGuire,
Thomas. "The Lockheed Martin Compact Fusion Reactor." Thursday
Colloquium. Princeton University, Princeton. 6 Aug. 2015. Lecture.
D. Park, J.
"High-EnergyElectron Confinement in a Magnetic Cusp Configuration."
Physical Review X.N.p., 11 June 2015. 06 Nov. 2015.
E. Wobig, H.,
T. Andreeva, andC.D. Beidler. "Recent Development in Helias Reactor
Studies." 19thIAEA- Fusion Energy Conference. IAEA FT/1-6, n.d. 04 Apr.
2016.
F. Wesson,
John; et al. (2004).Tokamaks. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-850922-7.
G. Spitzer,
Lyman. "TheStellarator Concept." Physics of Fluids (1958): n. pag. 4
Apr. 2016.
H. Perea, A.,
R. Martin, J.l.Alvarez Rivas, J. Botija, J.r. Cepero, J.a. Fabregas, J. Guasp,
A. LopezFraguas, A. Perez-Navarro, E. Rodriguez Solano, B.a. Carreras, K.k.
Chipley,T.c. Hender, T.c. Jernigan, J.f. Lyon, and B.e. Nelson.
"Description OfThe Heliac Tj-Ii And Its ecrh System." Fusion
Technology 1986 (1986):673-78.
I. Miller,
R.l., and R.a.Krakowski. "Modular Stellarator Fusion Reactor
Concept." Los AlamosLA-8978MS (1981): 1-161. 4 Apr. 2016.
J. Proc. of 20th International Stellarator-Heliotron Workshop (ISHW), Max Planck Institute, Greifswald,Germany. Greifswald, 2015.
K. Grieger, G.,
J. Nührenberg,H. Renner, J. Sapper, and H. Wobig. "HELIAS Stellarator
Reactor Studiesand Related European Technology Studies." Fusion
Engineering and Design25.1-3 (1994): 73-84. 4 Apr. 2016.
L. Haines, M.
G. "A Reviewof the Dense Z -pinch." Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion
Plasma Physics andControlled Fusion 53.9 (2011): 093001.
M. Jarboe, T.
R. "Review ofSpheromak Research." Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion Plasma
Physics andControlled Fusion 36.6 (1994): 945-90.
N. Slutz,
Stephen A., and RogerA. Vesey. "High-Gain Magnetized Inertial
Fusion." Phys. Rev. Lett.Physical Review Letters 108.2 (2012): n. page 4
Apr. 2016.
O. "Mirror
Systems: Fuel Cycles, loss reduction and energy recovery" by Richard F.
Post, BNES Nuclear fusion reactor conferences at Culham laboratory, September
1969.
P.
"Overview of LDX Results" Jay Kesner, A. Boxer, J. Ellsworth, I.
Karim, Presented at the APS Meeting, Philadelphia, November 2, 2006, Paper VP1.00020
Q. Krishnan,
Mahadevan."The Dense Plasma Focus: A Versatile Dense Pinch for
DiverseApplications." IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci. IEEE Transactions on Plasma
Science 40.12 (2012): 3189-221. Web.
R. Hedditch,
John."arXiv.org e-Print archive Physics ArXiv:1510.01788." Fusion in
a Magnetically-shielded-grid Inertial Electrostatic Confinement Device. ArXiv,
7 Oct. 2015. Web. 22 Dec. 2015.
S. Robert L.
Hirsch,"Inertial-Electrostatic Confinement of Ionized Fusion Gases",
Journalof Applied Physics, v. 38, no. 7, October 1967
T. Park, J.,
and R. A. Nebel."Periodically Oscillating Plasma Sphere." Physics of
Plasmas 12.5(2005): n. pag. AIP. Web. 22 May 2016..
U. Tuszewski,
M. "Field Reversed Configurations." Nuclear Fusion Nuclear Fusion
28.11 (1988):2033-092. Web. 22 May 2016.
V. Hsu, S. C.,
A. L. Moser, E.C. Merritt, C. S. Adams, J. P. Dunn, S. Brockington, A. Case,
M.
Gilmore, A. G.Lynn, S. J. Messer, and F. D. Witherspoon. "Laboratory
Plasma Physics Experiments Using Merging Supersonic Plasma Jets." J. Plasma
Phys. Journalof Plasma Physics 81.02 (2014): n. pag. Web. 22 May
2016..
W. A, Levine
M., Brown I. G, andKunkel. "Scaling for Tormac Fusion Reactors."
Scaling for TormacFusion Reactors. IAEA NIS, n.d. Web. April 1976..
X. Berkowitz,
J., K.o.Friedrichs, H. Goertzel, H. Grad, J. Killeen, and E. Rubin.
"CuspedGeometries." Journal of Nuclear Energy (1954) 7.3-4 (1958):
292-93. Web.16 June 2014.
Y. Barnes, D.
C., M. M. Schauer,K. R. Umstadter, L. Chacon, and G. Miley. "Electron
Equilibrium andConfinement in a Modified Penning Trap and Its Application to
PenningFusion." Physics of Plasmas Phys. Plasmas 7.5 (2000): 1693. Web. 22
May2016..
Z. Kodama, R.,
P. A. Norreys, K.Mima, A. E. Dangor, R. G. Evans, H. Fujita, Y. Kitagawa, K.
Krushelnick, T.Miyakoshi, N. Miyanaga, T. Norimatsu, S. J. Rose, T. Shozaki, K.
Shigemori, A.Sunahara, M. Tampo, K. A. Tanaka, Y. Toyama, T. Yamanaka, and M.
Zepf."Fast Heating of Ultrahigh-density Plasma as a Step towards Laser
FusionIgnition." Nature 412.6849 (2001): 798-802. Web.
.
AA. Nuckolls, John;
Wood,Lowell; Thiessen, Albert; Zimmerman, George (1972), "Laser
Compression ofMatter to Super-High Densities: Thermonuclear (CTR)
Applications" (PDF),Nature 239 (5368): 139–142,
Bibcode:1972Natur.239..139N, doi:10.1038/239139a0,retrieved August 23, 2014
BB. Laberge,
Michel. "AnAcoustically Driven Magnetized Target Fusion Reactor."
Journal of FusionEnergy J Fusion Energy 27.1-2 (2007): 65-68. 22 May
2016..
CC.
Meyer-Ter-Vehn, J."Inertial Confinement Fusion Driven by Heavy Ion
Beams." Plasma Phys.Control. Fusion Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion
31.10 (1989): 1613-628.Web. 22 May 2016.
DD. C,
Schuurman W., Bobeldijk,and R. F. De Vries. "Stability of the Screw
Pinch." Plasma Physics 11(1969): 1029. IOP. Web. 22 May 2016..
EE. Sykes,
Alan. "TheDevelopment of the Spherical Tokamak." ICPP,. Japan,
Fukuoka. 22 May 2016.Lecture..
FF. Jones,
Ieuan R. "A Review of Rotating Magnetic Field Current Drive and the
Operation of the Rotamak as a Field-reversed Configuration (Rotamak-FRC) and a
Spherical Tokamak (Rotamak-ST)." Physics of Plasmas 6.5 (1999): 1950-957.
Web. 11 Apr. 2017.
















I keep on hearing fusion people complain about investment into Fusion research in the US. Why not stop pulling on that dead horse, pick up your losses and move? Unless I'm mistaken, energy is a global issue, and not one of the US alone.
ReplyDeleteI know for a fact that there's a lot of different gov. subsidiaries available, both in local countries and in the EU as a whole. Funny fact is also that these grants usually stack.
For example, in the Netherlands alone, there's money available for energy, renewable energy, etc. from 100K (MIT) to multiple millions (MEI etc). With WBSO you get an extra subsidiary for income tax. See https://www.rvo.nl/subsidies-regelingen/subsidies-energie-innovatie for some details.
In the EU there are also multiple subsidiaries available. F.ex. see: https://ec.europa.eu/energy/en/funding-and-contracts
The reason US fusion researchers make noise about funding is convince our government to increase the funding. The US has better science talent than its' government deserves.
DeleteSure, but I believe fusion scientists feel very deeply that this should be researched. So if it's a local (country) problem, moving seems to be a logical course of action.
DeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDeleteThis comment has been removed by a blog administrator.
ReplyDelete